Watch Now: What Is a Diode?
Discover how diodes control current with one-way conduction. Learn about rectifiers, LEDs, and Zener diodes, and see their role in power regulation and signal processing through clear explanations and experiments!
What Is a Diode and How Does It Control Current?
A diode is one of the most fundamental components in electronic circuits. Its primary function is to control the direction of current flow, allowing current to pass in only one direction while blocking reverse flow. This prevents circuit damage and ensures proper operation. Diodes play a crucial role in rectification, signal regulation, overvoltage protection, and LED lighting. In this article, we will explore how diodes work, their different types, and their practical applications.
Basic Principles of a Diode
PN Junction and Unidirectional Conductivity
The core structure of a diode is a PN junction, formed by combining two different types of semiconductor materials:
- P-type semiconductor: Contains numerous holes (positive charge carriers) that attract electrons.
- N-type semiconductor: Contains a high concentration of free electrons (negative charge carriers).
When P-type and N-type semiconductors are joined, a depletion region forms at the junction. This region acts as an energy barrier, limiting the flow of charge carriers and regulating current conduction.
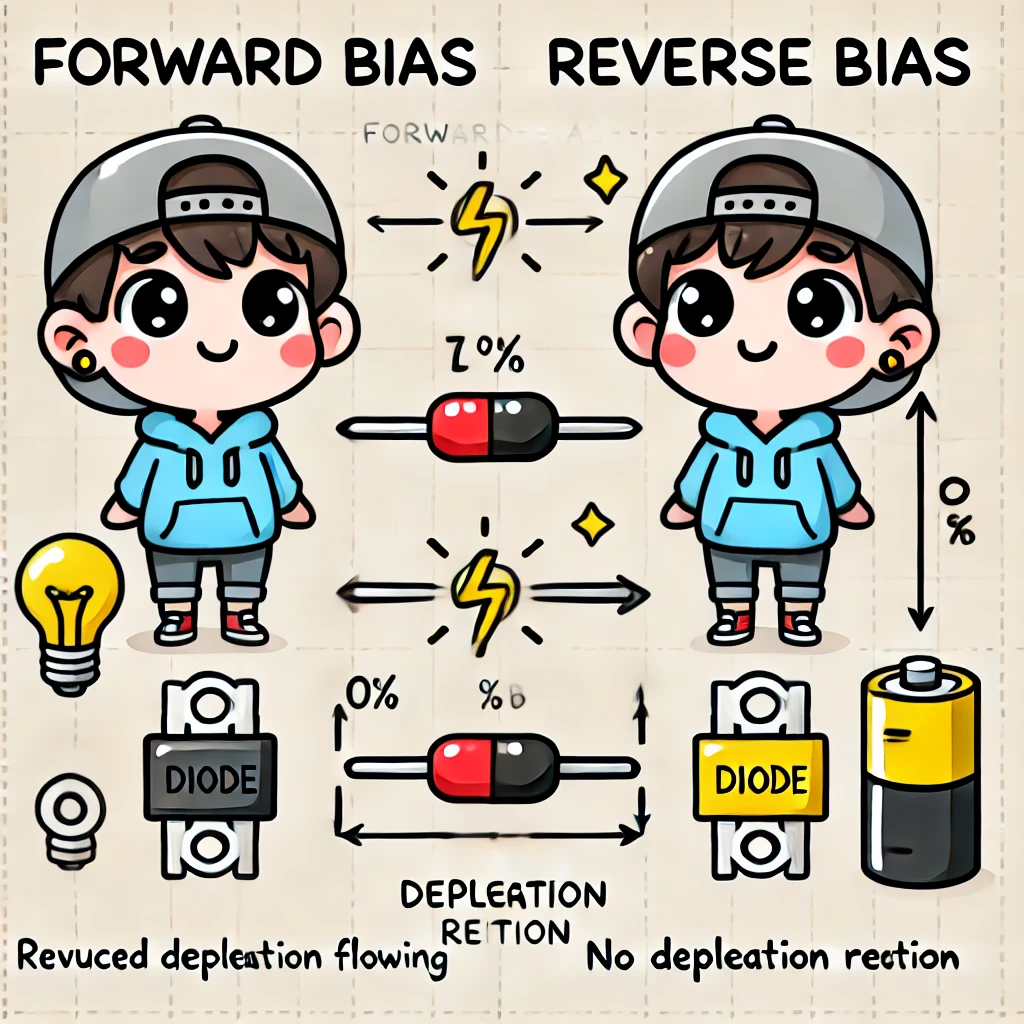
Forward Bias vs. Reverse Bias
- Forward Bias: When the P-side is connected to the positive terminal and the N-side to the negative terminal, the energy barrier decreases, allowing current to flow freely—diode is ON.
- Reverse Bias: When the P-side is connected to the negative terminal and the N-side to the positive terminal, the barrier increases, preventing current flow—diode is OFF.
This one-way conduction property makes diodes essential for controlling current direction in electronic circuits.
Types of Diodes and Their Applications
Different types of diodes serve various functions in electronic applications. Below are some common types and their uses:
1. Rectifier Diode
- Function: Converts AC (alternating current) into DC (direct current).
- Applications:
- Power supplies (AC to DC conversion)
- Transformer rectification circuits
2. Light Emitting Diode (LED)
- Function: Emits light when current flows through it.
- Applications:
- Displays, indicator lights, and lighting systems
- Automation sensors and optical communication
3. Zener Diode
- Function: Allows current to flow in reverse when a specific voltage is reached, stabilizing voltage and protecting circuits.
- Applications:
- Voltage regulation circuits
- Power surge protection
4. Schottky Diode
- Function: Features fast switching speed and low voltage drop, improving circuit efficiency.
- Applications:
- High-frequency applications (RF circuits)
- DC-DC converters
5. Photodiode
- Function: Converts light into electrical current, used for optical sensing.
- Applications:
- Light sensors
- Fiber-optic communication systems
Each diode type is designed for specific functions, making them essential components in modern electronics.

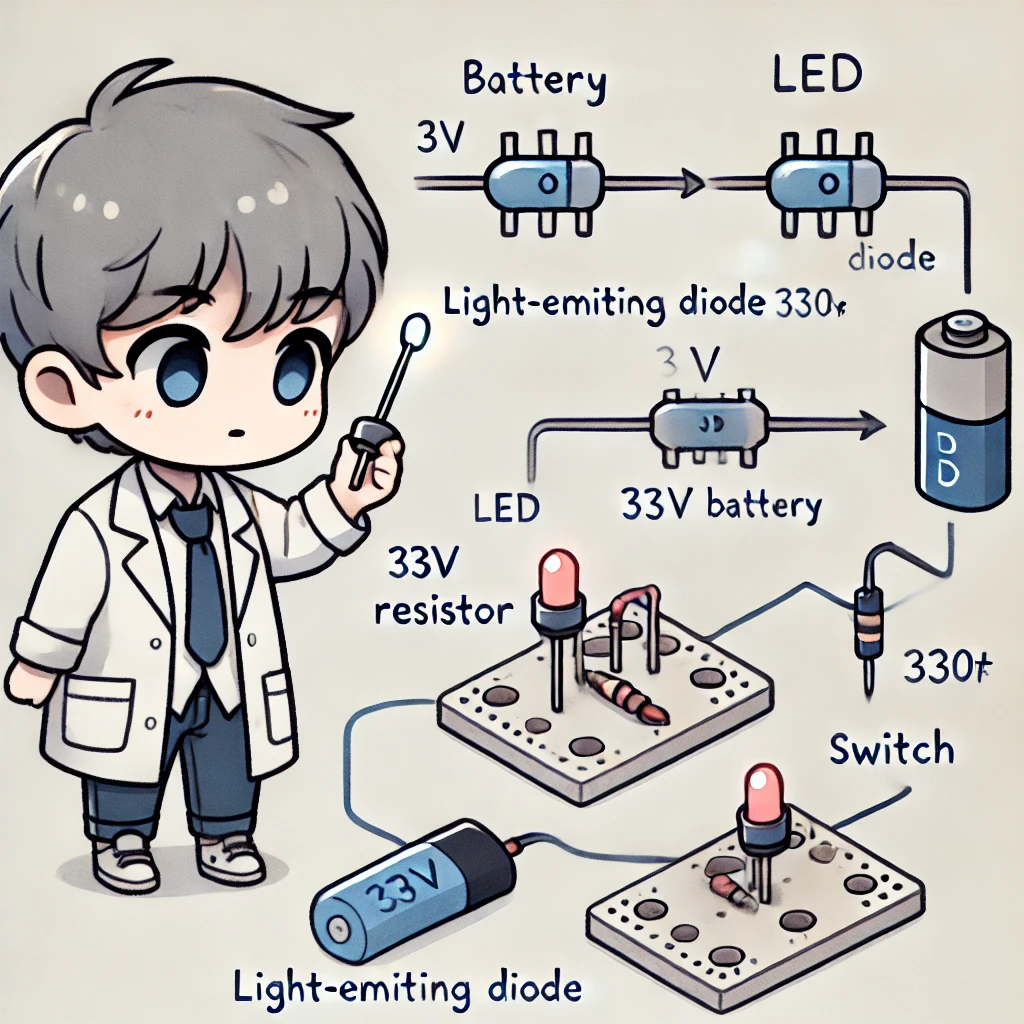
Simple Experiment: Observing the Unidirectional Conductivity of a Diode
You can use a basic circuit to test how a diode allows current to flow in only one direction.
📌 Materials
- LED (Light Emitting Diode)
- 3V battery
- 330Ω resistor
- Switch
- Connecting wires
📌 Steps
- Proper LED Connection: Connect the LED’s anode (long leg) to the battery’s positive terminal and the cathode (short leg) to the resistor, then connect the resistor to the battery’s negative terminal.
- Switch Control: Turn on the switch— the LED should light up.
- Reverse Connection Test: Flip the LED’s connection (anode to negative, cathode to positive) and observe— the LED should remain off.
🔎 Results & Analysis
- Forward Bias: The LED lights up, showing that current is flowing.
- Reverse Bias: The LED remains off, demonstrating that the diode blocks reverse current.
This experiment visually confirms the diode’s unidirectional conductivity, highlighting its role in rectification circuits and signal control.
Summary & Further Reading
Diodes are essential electronic components that use PN junctions to control current flow. Their wide range of applications includes power supplies, LED lighting, signal processing, and voltage regulation. Understanding how diodes work and their different types can help in designing and maintaining electronic circuits more effectively.
📌 Further Reading
🔹 [The Fundamentals of Circuits: Power, Wires & Load]
Explore the fundamentals of electrical circuits and how power sources and wiring impact device functionality.
🔹 [Current & Voltage for DIY Enthusiasts : Unlock the Basics]
A deep dive into voltage and current concepts, helping you understand how current influences diode operation.
🔹 [How to Design a Voltage Regulator? Applications of Zener Diodes] (Coming Soon)
Learn how Zener diodes stabilize voltage and protect electronic devices from overvoltage.
🔹 [The Future of LED Lighting Technology] (Coming Soon)
Discover the latest advancements in LED technology and its future applications.
💡 Have questions about diodes? Feel free to leave a comment or subscribe to our blog for the latest updates on electronic technologies! 🚀


